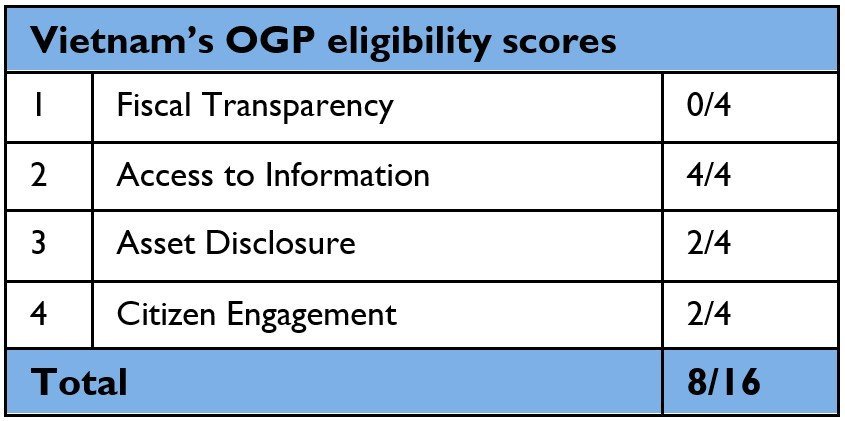
OGP’s eligibility data is updated by OGP Support Unit in the first quarter of each year, using the most up-to-date information from each data source available at that time. There are four OGP Minimum Eligibility Criteria.
1. Fiscal Transparency
The timely publication of essential budget documents forms the basic building blocks of budget accountability and an open budget system.
Measurement: Two points awarded for the timely publication of each of two essential documents (Executive’s Budget Proposal and Audit Report) for open budgets, using a subset indicators from the Open Budget Survey, conducted by the International Budget Partnership.
2. Access to Information
An access to information law that guarantees the public’s right to information and access to government data is essential to the spirit and practice of open government.
Measurement: 4 points awarded to countries with access to information laws in place, 3 points if a country has a constitutional provision guaranteeing access to information, and 1 point if a country has a draft access to information law under consideration. Countries with both a constitutional provision and a draft law under consideration will only be awarded the 3 points for the constitutional provision. Information taken from an ongoing survey by Right2Info.org (from the Open Society Institute Justice Initiative) and supplemented by the list at RTI-Rating.org (maintained jointly by the Centre for Law and Democracy and Access Info Europe).
3. Public Officials Asset Disclosure
Rules that require public disclosure of income and assets for elected and senior public officials are essential to anti-corruption and open, accountable government. It is also important to make the data publicly available so citizens can monitor the disclosures
Measurement: 4 points awarded to countries with a law requiring officials to submit asset disclosures that also has any requirement that the information should be accessible to the public, 2 points awarded to countries with a law requiring officials to submit asset disclosures, 0 points for no law on asset disclosure.
The source for the information on asset disclosures is the World Bank’s Public Officials Financial Disclosure database, which is updated on a rolling basis. The database is supplemented by a published survey the World Bank conducts periodically.
4. Citizen Engagement
Open Government requires openness to citizen participation and engagement in policymaking and governance, including basic protections for civil liberties.
Measurement: Using the EIU Democracy Index’s Civil Liberties sub-indicator where 10 is the highest and 0 is the lowest score, 4 points for countries scoring above 7.5, 3 points for countries scoring above 5, 2 points for countries scoring above 2.5, and 0 points otherwise.
Overall Scoring
Eligibility to join OGP is determined by evaluations of countries’ performance in these four critical areas of open government. Countries can earn a total of 16 points for their performance in these four metrics, or 12 points if they are not measured in one of the metrics. Countries that earn 75% of the applicable points (either 12 out of 16 or 9 out of 12) or more are eligible to join. As some of the indices OGP uses do not cover all countries, some countries are only measured on three criteria (and can earn up to 12 points).
Countries not assessed in a database for any of the metrics or those without recent updates are encouraged to provide additional information to the Support Unit. Any such information will be assessed independently by subject matter experts who will evaluate the submitted documents and evidence for participation to ensure that all OGP participating countries remain in good standing and that the performance measures are up to date. The OGP Support Unit works with this independent group of experts to review countries’ scores each year and posts the updated results to the OGP website. The Support Unit will inform the Steering Committee if a participating country falls below the minimum eligibility criteria at any point.
Values Check Assessment
In its September 20, 2017 meeting, the Steering Committee approved the implementation of a ‘Values Check’ assessment. Moving forward, countries will still need to score 75% or more on the current four Eligibility Criteria listed above, and, additionally, they also will need to pass a ‘Values Check’ before they are allowed to participate in OGP. This is an effort to ensure that new countries joining OGP adhere to the democratic governance norms and values set forth in the Open Government Declaration.
The source of the Values Check is the Varieties of Democracy ‘Dataset on Democracy.’ The dataset is compiled by 50 political scientists based on six continents analyzing 350 measures of each country’s democratic practices, supported by over 2800 local experts. For the Values Check, OGP employs two of V-Dem’s indicators:
12.2: CSO entry and exit – Measuring the extent to which the government achieves control over entry and exit by civil society organizations (CSOs) into public life, and
12.3: CSO repression – Measuring the extent to which the government attempts to repress civil society organizations (CSOs).
In the V-Dem dataset, countries are scored out of 4 on each measure. OGP has elected to consider the ordinal scores. To pass the values check, countries must score three or higher on at least one of the two V-Dem indicators.
The Values Check only applies to countries that are yet to join OGP and does not affect countries which have already joined.